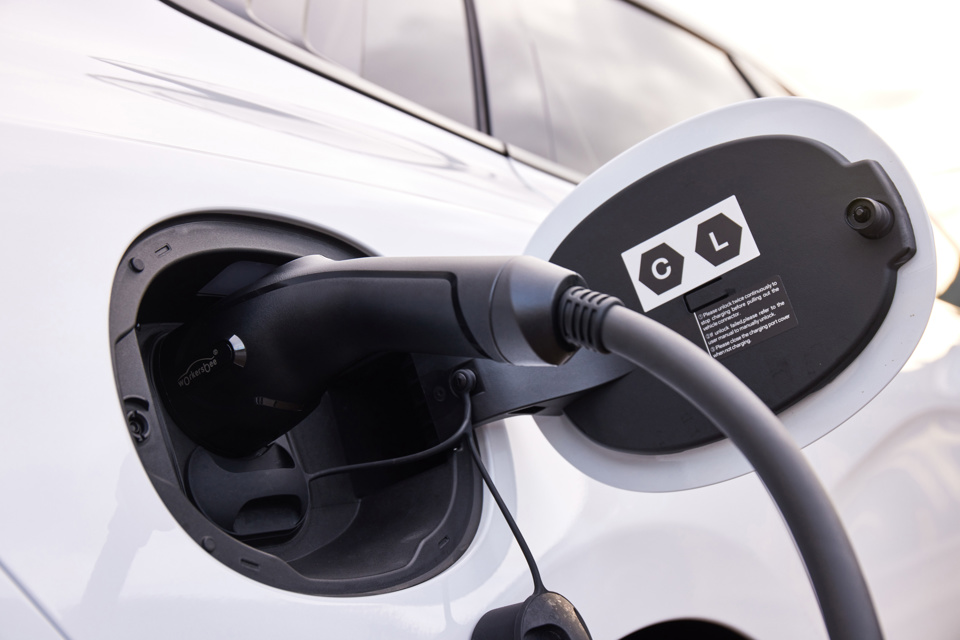
The UK has failed to hit its target of having six or more rapid or ultra-rapid electric vehicle chargers at every motorway service area in England by the end of 2023, new research conducted by the RAC shows.
Just 46 (39%) of 119 motorway services reviewed by the RAC on charging app Zapmap now have the target number of chargers above 50kW to serve the UK’s growing fleet of battery-electric vehicles which should have exceeded the 1 million milestone by the end of 2023. The number of rapid chargers has grown from just 27 (23%) at the end of April.
Commenting on the research, Sue Robinson, chief executive of the National Franchised Dealers Association (NFDA) which represents car and commercial retailers across the UK said that with the ZEV mandate coming into effect from this month, the Government needs to do more to increase confidence in consumers who are looking to switch to electric during this transitionary period.
“In our recent Consumer Attitude Survey, 57% of the respondents who stated they were not interested in purchasing an electric vehicle attributed this to a lack of charging facilities in the UK," she said.
Since the end of spring a further 178 high-powered chargers have been installed at motorway services. Positively, there are now more than 400 ultra-rapid chargers at services which means more than half (55%) can now offer some of the fastest possible charging speeds to drivers. Only 18 service areas have no rapid charging above 50kW, but worryingly four have no publicly accessible charging facilities whatsoever: Leicester Forest on both sides of the M1, Tebay South on the M6, and Barton Park on the A1(M).
There are now nearly 700 (693) Combined Charging System (CCS) connectors – the most common charging connector – at the 101 services offering high-powered charging, an increase of 225, or 48%. For the CHAdeMO connectors predominantly used by Nissan and Renault electrics cars, there are now almost 300 (282), up 32% compared to the end of April. Seventy per cent of all high-power motorway charging is now ultra-rapid, reducing the time drivers need to spend ‘filling up’ significantly.
The RAC said it was encouraged that there are now 14 services in England which have more than 12 such devices – up from only six in the spring. The Moto-run services at Exeter on the M5 has the most high-powered chargers of all motorway services, with 24 devices. Looking at all high-powered motorway chargers collectively, there are currently an average of five (4.9) devices at all 119 service areas in England – up from 3.4 at the end of April.
The Government’s target of having at least six rapid chargers above 50kW by the end of 2023, with some having more than 12 is set out in its ‘Taking charge: the electric vehicle infrastructure strategy’ published on 25 March 2022.
Its intention was to accelerate the roll-out of high-powered chargers on the strategic road network through the £950m Rapid Charging Fund so that EV drivers have confidence in the ability to undertake longer journeys, but it wasn’t until early December 2023 the Government announced it would be providing £70m in grants for a pilot scheme involving upgrades at 10 motorway service stations.
As of November 2023 charging statistics from Zapmap show the UK has 53,029 charging devices of which a fifth (19% or 9,992) are rapid or ultra-rapid. Looking at this figure against the RAC’s research reveals that only 6% (581) of all these high-powered chargers are at motorways services.
The Government says it expects there will be around 300,000 public chargers of all speeds as a minimum by 2030 and more than 6,000 high-powered chargers along strategic roads by 2035. Forecasts in the Competition and Markets Authority’s ‘Building a comprehensive and competitive electric vehicle charging sector that works for all drivers’ suggest that at least 280,000-480,000 public charge points will be needed by 2030.
RAC EV spokesperson Simon Williams said: “It’s clear from our research that the Government has fallen well short of its target of having six high-powered chargers at every motorway service area in England. While that’s the case, some very good progress has been made since the end of April when we last carried out our survey, with four-in-10 services (39%) now having met or exceeded the target number of chargers, compared to just under a quarter (23%) eight months ago.
“There is undoubtedly an eagerness among charge point companies and motorway service operators to install these types of units but unfortunately, it’s often the high-power cabling to the grid that’s the major barrier which is out of their hands.
“More clearly needs to be done to make this process simpler than it is currently. Hopefully once the Government’s Rapid Charging Fund kicks fully into action some of these hurdles will be overcome.
“We continue to believe that the wide availability of ultra-rapid charging is crucial in giving both current and future EV drivers confidence to know they can easily make journeys beyond the range of their vehicles in a time-efficient way.”
The NFDA said it welcomed recent announcements by the Government including the £70 million pilot scheme to boost the number of ultra-rapid chargepoints at motorway services but added that there is still more that needs to be done.
“As we enter the new year, the UK government needs to ensure that it meets targets to meet increasing consumer demand for electric vehicles," said NFDA chief Sue Robinson, who added, "2024 looks set to be a busy year with the Spring Budget already being announced for 6 March and with an election date yet to be set. NFDA will monitor key developments throughout the year on behalf of its members.”




















Login to comment
Comments
No comments have been made yet.